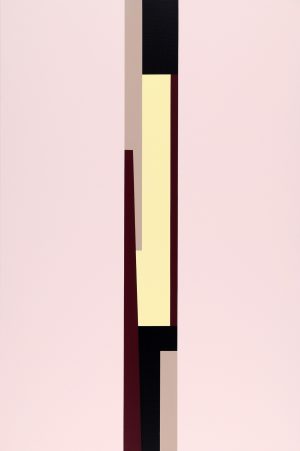Imre BAK
Current Situation
- Year(s)
- 2013
- Technique
- acrylic on canvas
- Size
- 80x120 cm
Artist's introduction
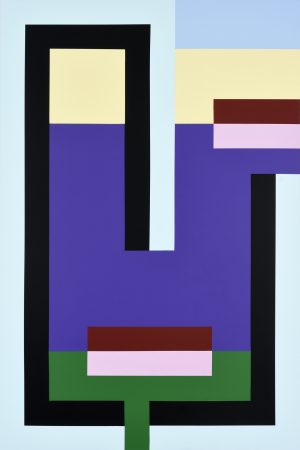
Imre Bak established the specific character of his paintings in the mid-1960s, referencing the lessons of Geometric Abstraction to this day. Along with some of his contemporaries, Bak defied the geopolitics of the era and the existential and further difficulties arising from the existing social order to connect with the global art of the time. During the Iparterv exhibitions (1968–1969), Bak had already formulated the idea of combining the American tendencies of Hard-edge painting and Minimalism with motifs inspired by Hungarian folk art and the traditions of the local avant-garde. This structuralist programme – which consciously examined the nature of signs and symbols – defined his paintings from the 1970s. In the 1980s, the geometric system of Bak's paintings became increasingly complex, leading to the postmodern turn in the artist's work. During the 1990s, Bak's motifs shifted towards "simplification" again, as expanded surfaces of colour started to define his architecture-inspired paintings. In this period, Bak used perspective and a set of geometric elements to construct his landscapes, where the predominant motifs were "structures" consisting of architectural elements. In his latest work conceived after the 2000s, Bak returns to Geometric Abstraction's fundamental question of how spatial illusion is elicited through two-dimensional means. His compositions that combine rectangular fields of colour with dichromatic, meanderlike lines are based on the utilisation of pure, intense colours, which create the illusion of depth on the canvas. Áron Fenyvesi
More artworks in the artist's collection »